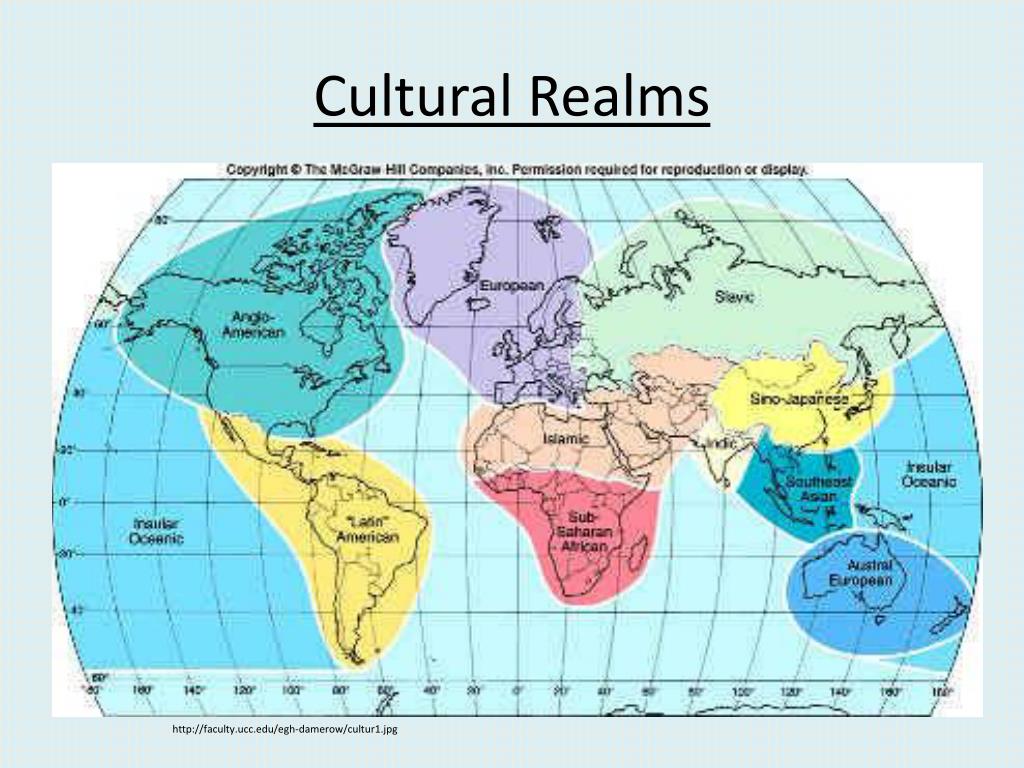
Cultural realms are vast landscapes of human expression that transcend geographical boundaries, forming intricate tapestries woven from the threads of tradition, belief, and communal identity. In AP Human Geography, cultural realms serve as a crucial framework for understanding the complexity of human culture and its varied manifestations across the globe. They act like ecosystems, where distinct elements coexist, interrelate, and sometimes clash. By delving into these realms, students glean insights not only into cultural diversity but also into the profound implications of globalization and environmental concerns.
To encapsulate the notion of a cultural realm, consider the metaphor of a grand tapestry. Each thread represents a cultural trait—language, religion, culinary practices, and social customs—weaving a unique pattern that reflects the ethos of a particular group. When examined through the lens of AP Human Geography, it becomes apparent that these realms are not static; rather, they are dynamic, influenced by historical movements, migration patterns, and the omnipresent forces of modernization.
At the core of understanding cultural realms is recognizing that they are often delineated by shared characteristics. For instance, the Latin American cultural realm distinguishes itself through a blend of indigenous traditions and Spanish colonial influences. This hybridization manifests in the region’s languages, like Spanish and Portuguese, as well as in art forms ranging from vibrant folk dances to the melancholy strains of tango. Each of these elements contributes to a collective identity, echoing the narrative of resilience and adaptation.
Yet, the narrative does not end there. As these cultural traits diffuse into other realms, they not only retain vestiges of their origins but also acquire new dimensions. The spread of Latin American music genres, such as salsa and reggaeton, into North American pop culture exemplifies the richness of cultural exchange. This phenomenon, often labeled “cultural syncretism,” indicates an ongoing dialogue between cultures, showcasing how they borrow, reinvent, and sometimes resist elements from one another.
Analogous to how a river carves through a canyon, cultural realms are shaped by geographical boundaries yet remain fluid in their interactions. In AP Human Geography, examining the African cultural realm unveils a rich mosaic of ethnic groups, languages, and practices. With over 3,000 distinct ethnic groups, Africa’s cultural landscape is as varied as its geography, ranging from the vast Sahara Desert to the lush rainforests of the Congo. This exquisite diversity poses both challenges and opportunities for unity and cooperation among nations.
The notion of cultural realms extends beyond mere classification of traits; it invites introspection into the philosophical underpinnings of what it means to belong. Consider the Eastern cultural realm, encompassing regions influenced by major philosophies such as Confucianism and Buddhism. These belief systems permeate not just individual lives but also govern societal interactions and governance. They emphasize harmony, community, and a deep-seated reverence for nature, fostering a sustainable approach to existence. As climate change grows more pervasive, such cultural values may hold the key to fostering eco-conscious habits.
The analysis of cultural realms undeniably circles back to the environment. Cultural practices often arise from the landscapes that individuals inhabit, illustrating a symbiotic relationship between people and their surroundings. Thus, environmental degradation and climate upheaval pose significant threats, not only to biodiversity but also to cultural identities. The loss of traditional agricultural practices, for instance, has been felt across many cultural realms where climate change disrupts the delicate balance that sustains both ecosystems and livelihoods.
Moreover, globalization acts as a double-edged sword in the realm of culture. While it fosters connectivity and exchange, it may concurrently dilute distinct cultural identities. The proliferation of multinational corporations and Western media poses a risk of cultural homogenization, where unique traditions fade into obscurity. The consequence is akin to a painting where the vibrant colors of provincial cultures are washed away, leaving only a monochrome canvas devoid of character and depth. It is imperative to approach globalization with a discerning eye, championing cultural preservation while embracing the enrichment that cross-cultural interactions can bring.
In the face of these challenges, nurturing awareness and appreciation for cultural realms becomes crucial. Educational frameworks such as AP Human Geography serve as platforms for enlightenment, fostering critical discussions about the interplay between culture and environment. Students are equipped with analytical tools to explore how cultural realms contribute to global issues, ranging from biodiversity conservation to sustainable development. By understanding the nuances of different cultures, individuals can cultivate a deeper empathy for the plights of communities affected by environmental crises.
Ultimately, cultural realms represent not just a map of human diversity but also a reflection of collective aspirations and values. The interplay between climate change and culture is a poignant reminder that humanity must navigate these intricate relationships with care and respect. As we confront the escalating threats to our planet, let us draw inspiration from the resilience embodied in diverse cultures. By embracing the tapestry of human existence, we can forge pathways toward sustainable futures that honor both the Earth and its myriad inhabitants.
As we continue to explore these rich cultural landscapes, we must commit to preserving the unique appeal of each realm, understanding that it is through our shared narratives and experiences that we can effectively address the pressing issues facing our global community. The persistence of cultural identity amidst transformation is not merely a relic of the past but a vital force propelling us toward a more sustainable and compassionate future.